Exploring the Advantages of Nuclear Energy
17 Nov, 20238 minIn the ever-evolving landscape of energy production, the quest for cleaner and more sustaina...

In the ever-evolving landscape of energy production, the quest for cleaner and more sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels has taken centre stage. Among the contenders in this pursuit, nuclear energy is a potent player with a rich history dating back to the mid-20th century. In this guide, we delve into the intricate world of nuclear power and the advantages of nuclear energy.
Our guide will begin with answering the fundamental question: What is nuclear energy, and how does it function? From the core of an atom to the mechanisms of nuclear fission, we will uncover the science behind this powerful energy source. We will then address another pivotal question: Is nuclear energy renewable or non-renewable? While the answer may seem straightforward, the reality is nuanced, with implications that extend far into our energy future.
We will then explore the key advantages of nuclear energy, from its unparalleled energy density to its unwavering reliability, cost-effectiveness, and remarkable position as a low-carbon solution that can positively impact the world's climate change and net zero efforts.
In this guide, we will uncover the following:
- What is nuclear energy?
- How does nuclear energy work?
- Is nuclear energy renewable or non-renewable?
- What are the advantages of nuclear energy?
What is nuclear energy?
Nuclear energy has been a significant player in the global energy space since the first nuclear plant began operations in 1950s Russia, later growing prominence in the 1960s to the end of the 1980s. Fast forward to today, and nuclear power has the potential to be a clean energy alternative to fossil fuels and a significant contributor to the 2050 net-zero targets.
Nuclear power originates, from the energy stored in an atom's core, otherwise known as the nucleus. It’s released to produce electricity when these atoms are split apart in a process called nuclear fission or when they are fused in a reaction referred to as nuclear fusion.
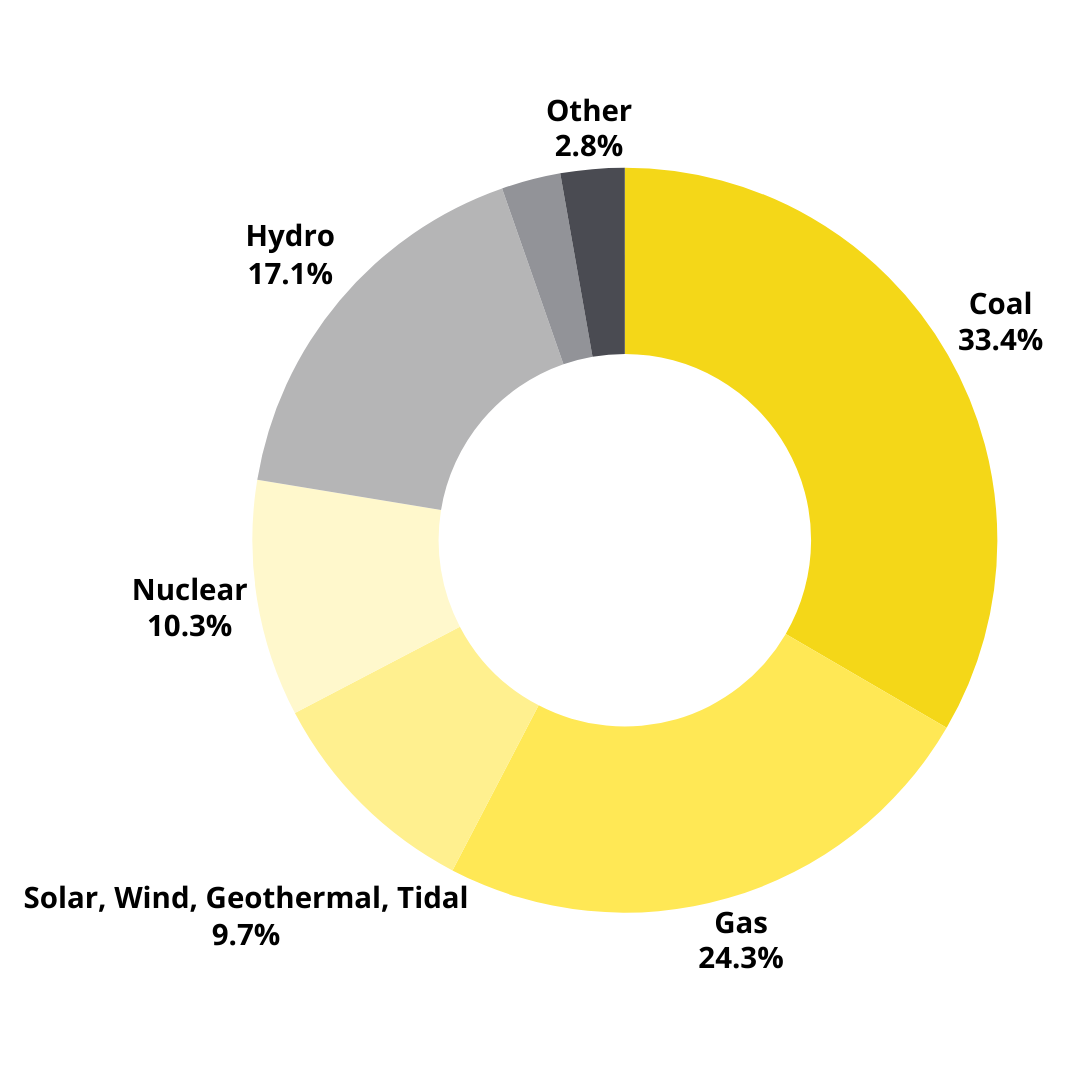
Source: World Nuclear Association
Studies have stated that nuclear energy makes up around 10% of the world's electricity output from 440 nuclear power stations. Behind hydropower, it is the planet's second-largest source of low-carbon electricity. Additionally, more than 50 countries are utilising the advantages of nuclear energy.
How does nuclear energy work?
Commercially, nuclear energy is produced through nuclear fission - a reaction produced in a nuclear power plant or nuclear reactor. The reaction occurs when a neutron particle collides with the nucleus of an atom, typically uranium-235.
When this collision happens in the nuclear reactor, the atom’s nucleus is split into two or more smaller nuclei to cause a chain reaction that releases vast amounts of heat. The heat is then combined with a coolant, typically water, to create pressurised steam. This steam is used to power turbines that spin to produce electricity.
Here’s a step-by-step process of how nuclear energy works in a reactor:
- The reactor core is loaded with fuel rods. The reactor core is a large vessel that contains fuel rods and other components needed to create nuclear fission. These fuel rods contain uranium pellets, which are the atomic materials typically used in the fission process.
- The reactor core is inserted with control rods. Control rods absorb neutrons, which slows down the nuclear fission chain reaction and controls the reactor's power output.
- The nuclear reactor is started. Once the control rods are withdrawn, the nuclear fission chain reaction begins.
- Nuclear fission occurs. When a neutron collides with the uranium atom, it causes the atom to split into multiple and smaller atoms. This process releases a significant amount of energy and two or three more neutrons. The neutrons released can then split other uranium atoms, creating a chain reaction.
- Heat is transferred to a coolant. Heat is released from nuclear fission and transferred to a coolant, typically water. The coolant circulates through the reactor core and absorbs the heat.
- The coolant is heated and pressurised. The coolant is heated to a very high temperature and pressurised, causing the coolant to turn into steam.
- Steam drives a turbine. Steam produced between the heat and coolant is piped to a turbine. The steam helps to spin the turbine, which is connected to a generator to produce electricity.
- The steam is condensed back into water. After the steam has driven the turbine, it is condensed back into water and reused in the reactor to restart the process.
As nuclear fission is a continuous process, nuclear reactors can produce electricity 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. The process commonly occurs in a pressurised water reactor (PWR), however, it can also take place in a boiling water reactor (BWR). The main difference between a pressurised water reactor (PWR) and a boiling water reactor (BWR) is how they produce steam.
In a PWR, the water coolant in the reactor core is kept under high pressure, preventing the water from boiling despite being heated to a very high temperature. The heat from the water is then transferred to a secondary circuit, turning water into steam to drive the turbine and generate electricity.
Alternatively, in a BWR, the water coolant in the reactor core is allowed to boil. The steam produced in the core of the reactor is then separated from the water and sent to the turbine to generate electricity. Both systems are reliable and produce the same outcomes.
Nuclear energy can also be produced via nuclear fusion. Here, the theory is that two atoms are fused to create a vast amount of energy, four times greater than the amount produced by nuclear fission. For example, the sun is a giant fusion reactor, self-regulated by hydrogen atoms that fuse to make helium.
However, nuclear fusion is not commercially safe or scalable as a viable alternative to nuclear fission. Scientists have been working on this alternative solution since the 1930s and have only managed to recreate the reaction for a matter of seconds in a lab setting.
Progress is being made to make nuclear fusion a commercially usable solution, with the ITER project in France currently in the assembly stage since 2020 to produce the largest nuclear fusion facility in the world. The project aims to replicate the complex reactions that power the sun to demonstrate that nuclear fusion can generate energy on a commercial scale.
Despite the future of nuclear energy leaning towards alternative solutions, nuclear fission is the only commercially viable option.
Is nuclear energy renewable or non-renewable?
Despite being a source of clean energy, Nuclear Power is considered a non-renewable energy source. Unlike renewable energy sources that can be forever replenished, the fuel used in nuclear power plants, typically uranium, is a finite resource that cannot be replenished naturally.
Once all the uranium on Earth is used up, no more nuclear fuel will be available. However, experts believe nuclear energy could be around for the foreseeable future, with various sources stating it could be used until 2060.
Despite not being a fully renewable energy source, nuclear power is often considered in the conversation of alternative and renewable energy. Similarly, to renewable solutions, such as wind, solar and hydrogen, nuclear energy does have its benefits towards positively benefiting climate change.
For example, no greenhouse gases are generated when nuclear energy is produced. Additionally, as mentioned earlier, nuclear power is the world’s second-largest source of low-carbon energy behind hydrogen, making up 10% of the global electricity output.
Of course, there are ongoing challenges surrounding the fact that nuclear energy does produce radioactive waste, which must be safely stored and left undisturbed for thousands of years for it not to cause harm to the global population or the environment.
These challenges are being tackled daily to make nuclear power production 100% safe. Despite these concerns, nuclear energy should still be considered a valuable alternative energy solution that provides jobs for talented individuals and helps to power businesses, households and the planet.
Moreover, nuclear energy can be an additional solution to support renewable efforts. It can act as an assistant to the growing need for renewable power to meet global electricity demands and help the planet reach net zero targets.
What are the advantages of nuclear energy?
There are many advantages of nuclear power, from having a high energy density, being a reliable energy source, and a cost-effective and low-carbon solution, here are the top advantages of nuclear power.
Nuclear power has a high energy density
One of the most prominent advantages of nuclear energy is its high energy density. What is meant by nuclear fuel having a high energy density is that it can store tremendous amounts of energy in a small volume. This makes it ideal for transportation and other applications where space is limited.
With the capacity to generate high levels of power, the energy produced in a nuclear fission reaction is estimated to be 10 million times greater than what can be released when fossil fuels are burned.
Moreover, the amount of nuclear fuel needed in a nuclear power plant is far less than in other types of power plants. Nuclear energy has the capacity to support large-scale demands for electricity. In fact, a minimal amount of uranium fuel has the potential to produce 1000s of megawatts, enough to generate enough electricity to power a city with a population of around 500,000 people. Therefore, it’s no surprise that nuclear power makes up nearly 20% of the electricity generation in the US alone.
Nuclear power is a reliable energy source
The next advantage of nuclear energy is its reliability. Nuclear reactors and power plants can operate 24/7, all year round, regardless of weather conditions and external climatic factors. Due to nuclear power production being constant and practically unaffected by any constraints, organisations within the industry can expect to see excellent annual ROIs. Because of this, engineers operating within nuclear energy can benefit from the permanent vacancies that are always required.
Further emphasising the reliability of nuclear energy is its capacity factor and having a stable baseload of electricity. Capacity factors of 100% correlate to a plant's ability to produce energy constantly. Nuclear plants have the highest capacity, typically hitting the 90% mark. For context, this is almost twice as much as plants that are powered by natural gas (54%) and coal (49%) and nearly three times greater than wind (34%) and solar (24%).
Nuclear energy costs less to produce
Another one of the top advantages of nuclear energy is that it costs less to produce than other energy sources, particularly fossil fuels. Although the initial construction of nuclear reactors and plants is expensive, the operational costs are 33% to 50% cheaper than coal and 20%-25% of a gas combined-cycle plant.
Additionally, the cost of uranium required for nuclear fission is also low when factoring in that only a small amount is needed to produce tremendous amounts of power. It’s also low compared to the cost of running a nuclear power plant.
Moreover, the lifespan of a nuclear plant is around 40-60 years, if not longer. Therefore, when considering the building and operational costs, the monetary value made by nuclear plants outweighs other associated outgoing expenditures.
Nuclear energy is a low-carbon solution
Nuclear energy produces less pollution than fossil fuels. Aside from the radioactive waste, nuclear power has been proven to be a low-carbon source of energy that produces zero greenhouse gases.
Additionally, nuclear energy saves over 470 million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide each year that would otherwise be produced by fossil fuels. To give this statistic further perspective, according to NEI, this roughly equates to taking 100 million passenger vehicles off the road.
Due to its low-carbon and zero greenhouse gas emissions, nuclear energy is, in effect, supporting the efforts to keep our air clean. Nuclear power is essentially helping to prevent harmful pollutants from entering the atmosphere that can cause smog and acid rain to even health problems such as cardiovascular disease and lung cancer.
Due to its ability to reduce the world’s reliance on fossil fuels and help power the energy transition, nuclear energy is a clear frontrunner for addressing climate change.
Our final thoughts on the advantages of nuclear energy
Ultimately, the advantages of nuclear energy reveal that it is a promising and valuable source of power that can support our quest for a sustainable future. Nuclear energy, harnessed through processes like nuclear fission, offers a high energy density, making it a compact and efficient solution for our energy needs. With the ability to operate continuously regardless of external conditions, its reliability ensures a stable source of electricity for decades to come.
Furthermore, nuclear energy's cost-effectiveness, with low operational costs and long power plant lifespans, positions it as an economically viable energy solution. Additionally, its significant contribution to reducing carbon emissions and greenhouse gases demonstrates its commitment to environmental stewardship.
While nuclear energy is not considered renewable due to finite resources such as uranium, its role as a low-carbon alternative cannot be understated as a way to support the energy transition. Of course, it comes with challenges, such as radioactive waste management, but these are being addressed to enhance safety and sustainability.
As we work towards a cleaner, more sustainable future, nuclear energy should be recognised as a crucial component of the solution. Its energy density, reliability, cost-effectiveness, and low environmental impact advantages make it an essential contributor to the effort to combat climate change and achieve net-zero targets.
Looking to grow your career in renewable energy?
With a cumulative experience of over 90 years, we specialise in connecting the world's most innovative organisations with the best talent on the market. We deliver unrivalled permanent and contract jobs to support your future careers in the energy sector, allowing you to truly harness the advantages of nuclear energy.
Our global expertise spans 45 countries and over 80 offices, so no matter where you are in the world, we can find the job best suited to your needs. If you’re seeking the latest nuclear energy jobs, register here today.