Life Science in 2023 - Research and Development Insights
20 Mar, 202310:12As the world continues to face numerous health challenges, the importance of the Life Scien...

As the world continues to face numerous health challenges,
the importance of the Life Science industry has only increased. The industry
has been instrumental in developing ground-breaking treatments and cures for
various diseases, and it continues to push boundaries in terms of innovation
and discovery.
Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data have
transformed research, allowing more accurate and efficient drug discovery
processes. Additionally, the development of precision medicine, which uses
patient-specific data to tailor treatments, has upended traditional approaches
to healthcare and opened new avenues for personalised care.
The industry has seen a surge in the development of gene
therapies and immunotherapies, which have shown promising results in treating
previously untreatable diseases. Another area of innovation is the development
of biosimilars, which are biological drugs like existing treatments but offered
at a lower cost.
Despite the many advancements and innovations in the Life Science
industry, some challenges must be addressed. One such challenge is the high
cost of developing and bringing new drugs to market. The lengthy and expensive
regulatory process can deter companies from investing in research and
development, limiting the number of new treatments available to patients.
Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need for increased
collaboration and coordination between industry stakeholders and regulatory
bodies to ensure the timely development and distribution of vaccines and
treatments.
Current challenges faced by life sciences companies
A continued lack of talent in a growing market – The
life science industry is experiencing a shortage of skilled professionals
despite its growth. As companies expand and aim to have a diverse range of
products, the necessary skills and experience to develop them are not keeping
up with the demand for talent. This is happening despite the increasing
popularity of employee benefits such as flexible and remote work arrangements.
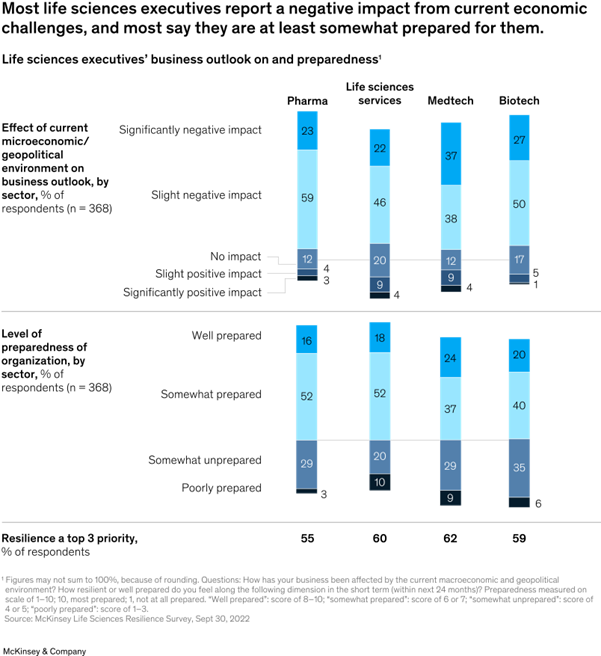
Increased costs – The Life Sciences industry has been
facing a decline in its operational costs and profits due to the combined
impact of high inflation and energy expenses. This trend has persisted even
during the COVID-19 pandemic, where less than one-fourth of the organisations
surveyed in the 2022
McKinsey Life Resiliences Survey felt adequately equipped to handle these
challenges. As a result of reduced margins, companies are being more careful
with their investments and emphasising preparation to tackle future obstacles
in the post-pandemic economy.
Supply chain issues – The economic downturn has
impacted all parts of the supply chain. There has been a rise in materials
costs as certain countries have experienced shortages, and transport expenses
increased due to the fuel crisis in 2022. Even though these shortages and costs
have decreased in 2023, their ripple effects are still noticeable. On the
consumer end of the supply chain, inflation has led to changes in spending
habits. Many customers are now seeking more affordable and efficient means of
obtaining products to reduce their expenses. This shift in consumer behaviour
has resulted in lower revenue and sales for life science companies, which may
need further cut costs.
ESG strategies are critical – The combined impact of
public opinion on climate change and environmental protection, legal changes,
and the need for cost-cutting has compelled businesses to adopt Environmental,
Social, and Governance (ESG) strategies. An instance of this is the US Uyghur Forced Labor
Prevention Act of April 2021, which prohibits importing products made or
partially made in China’s Uyghur region. A similar measure was enacted in the
UK in 2022. Live science businesses must now be transparent and accountable for
implementing their ESG strategies, with the associated costs being a crucial
factor in their transformation efforts.
Investment in technology to better products more rapidly –
In today’s world, the significance of technology in life sciences cannot be
ignored. The life sciences industry has been dramatically influenced by the
rapid production of the COVID-19 vaccine, which has created a standard for
other companies to follow. As a result, businesses are compelled to invest in
technology at every stage. The life sciences sector is being propelled forward
by artificial intelligence and data technology advancements, which necessitate
significant investment. Companies are seeking the most effective solutions to
stay ahead of the competition as consumer needs rise.
The role of innovation in life sciences research and development
In the life sciences industry, organisations must possess
the ability to innovate. Our knowledge of biology and the human environment
constantly evolves as discoveries are made. It is necessary to refine and
enhance the effectiveness of medicines while minimising their side effects. In
addition, the development of drugs and therapies and the growth of the ageing
population are becoming increasingly important. The COVID-19 pandemic has
highlighted the importance of innovation, as teams worldwide collaborated to
find a vaccine quickly. Without creation, this achievement would not have been
possible. Moreover, innovation is essential for long-term competitiveness. In
the next decade, major pharmaceutical companies will lose
exclusive rights to 15 top-selling drugs, which could result in a potential
revenue loss exceeding $100 billion.
Emerging technologies and innovations
Big data
Life sciences have always been heavily dependent on data,
with huge amounts of large and complex data produced every minute by thousands
of researchers across the globe. The COVID-19 pandemic generated vast amounts
of data to develop a vaccine in record time, further highlighting the critical
importance of big data in the life science industry.
In a survey by NewVantage
Partners in 2022, 50% of life science companies reported increased
investment in data, with all surveyed organisations claiming to be fully
committed to further initiatives. As a result, the global life sciences
analytics market is set to grow at a CAGR of 11.83% to $15.95bn by 2025.
There are many advantages to the big data revolution;
·
Faster research – One of the key problems
data scientists face is the time-consuming process of gathering and analysing
complex data. Big data supports researchers by pooling this data and studying
trends, lowering the time to approve new drugs.
·
Using data trends to inform investment
decisions – By collecting patient information, big data can be used to
analyse the needs of a particular demographic, informing investment decisions
on new research.
·
A better understanding of risk – With
more data on previous trials and research, data scientists can run more
iterations of risk assessment, enabling a more thorough evaluation in less
time.
·
Significant improvements in clinical trial
data – Data scientists spend less time gathering and understanding data and
more time creating new analyses and exploring the data. These improvements allow
for a quicker, more in-depth understanding of drug development and real-world
patient research.
A.I.
Big data goes hand in hand with A.I. – the ability to trawl
vast amounts of data for trends and information to produce new analyses
quickly. A.I. has taken a huge leap forward within the last year. The most
well-known development recently is Microsoft and OpenAI’s ChatGPT, capable of
answering complex queries with real-world data.
Technology is advancing quickly and is driving the life
science industry. Data scientists can test theories and query data using
complex requests, drawing insights from big data and producing accurate
analytics for data scientists to draw recommendations on.
There are other advantages outside of research;
·
Clinical trials – A.I. can estimate
sample size and plan the deployment of trials
·
Disease diagnosis – frontline medical
staff can input symptoms and patient data, and A.I. can suggest possible
diagnoses quickly based on data models
·
Logistics – A.I. can also be used to
forecast demand for products and manage logistics accurately, reducing
overheads and logistics costs
·
Increasing healthcare access – A.I.
medical support and ‘telemedicine’ supports less trained medical workers in
diagnosing and treating patients where the resource is unavailable. This is
particularly helpful when there is a lack of trained professionals, resulting
in limited healthcare access.
Richie Bavasso, Co-Founder and
CEO of nQ Medical, recently
said in a Forbes article on A.I.;
I’m excited by the advancement of
synthetic data allowing my data science team to feed our machine learning (ML)
models with data to simulate large populations of people with diseases.
Synthetic test data allows us to reflect on ‘what if’ scenarios, making it an
ideal way to test a hypothesis. It is a more accurate, scalable, and
economically feasible replacement for real-world records to generate large
training datasets and reduce restrictions with the use of sensitive data.
Nanotechnology
Research in the industry is looking at diseases at a
molecular level in real-time to develop new therapies and cures for conditions
that have previously been difficult to treat.
Nanotechnology is being developed to generate new
possibilities for delivering medication. Disease biomarkers are being improved
through the help of nanoscale sensors that have more accuracy.
Nano-bioengineering is aiding in the formation of new treatments for sickness
with the use of artificial biomolecules or through tissue regeneration.
In the arena of infectious diseases, nanotechnology is
yielding productive results, which will be used in treatments for malaria,
tuberculosis, and HIV. These disorders have a high mortality rate and have
proven difficult to treat. Scientists are now concentrating on creating
nano-sized vessels for new and existing remedies as a fresh approach to
addressing the issues typically linked to treating these conditions.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is a new, advanced
branch of medicine that attempts to use gene alteration to treat or cure
various illnesses, including cancer, genetic disorders, and certain infectious
diseases. In the United States, the first gene therapy was approved by the FDA
in 2017, and since then, there have been more
than 20 cell and gene therapies given the green
light.
The Alliance for Regenerative
Medicine forecasts that five novel gene therapies for rare diseases should be
available by 2023, such as those for sickle cell disease, Duchenne muscular
dystrophy and haemophilia.
The development of these
therapies has challenged life sciences organisations to consider changing their
business models. They must consider how they will identify which people will be
suitable for the treatments, acquire blood samples for the therapies, and
negotiate with insurers for reimbursement. Additionally, they will have to
develop a system for tracking the results of the treatments for outcome-based
contracts. These questions, and many more relating to payment, customer
experience, supply chain, and manufacturing, must be addressed.
The development and usage of
precision health are driven in part by the rise of next-generation DNA
sequencing (NGS). This technology is moving out of the lab and into healthcare,
providing improved care and outcomes for a broader population. NGS offers large
amounts of data, speed, and scalability, allowing for a more comprehensive
range of applications than ever before. The Illumina NovaSeq X sequencer,
released in 2022, is an example of a machine capable of sequencing 20,000
genomes in a year at $200 per genome. As the cost of sequencing genomes
decreases, delivering personalised healthcare and gene therapy on a larger
scale becomes easier.
The role of digital health in the life sciences industry
The days of handwritten medical notes are gone; today,
almost all medical health records are kept electronically, accessible by health
professionals and kept up-to-date. Records are complete, often more detailed
than before, and supported by a scaled global infrastructure.
Digital health has grown exponentially in recent times.
According to a
recent survey by Accenture, 35% of individuals now access health services
through virtual consultations versus 6% before the pandemic.
Smartphone apps have been the first step, with health-tracking
apps connected to medical services and databases of self-help information to
support individuals. Some of these apps, developed by healthcare organisations,
offer online virtual consultation, again ensuring a central point of information
gathering for organisations looking to gather valuable data to build products
and market them correctly.
There are also emerging opportunities. Wearable technology,
such as smartwatches, have been around for many years and have had basic
functionality to track movement and heart rate. Other devices, such as heart
monitors and continuous blood glucose monitoring technology, are also widely
used. As this technology continues to advance, gathering day-to-day patient
data. This technology can then advise those individuals on their health status,
collect data for A.I. in apps to analyse, and suggest any health issues they
have recorded to the wearer.
This technology is fundamental in bridging the gap between the most remote or under-supported locations, where healthcare support and advice may be less readily available. Regions where healthcare is difficult to provide in person, can be supported through digital technology, improving healthcare, slowing the spread of contagious viruses, and gathering even more global data to drive new research and development.
How NES Fircroft is supporting candidates to the Life Science industry
NES Fircroft has supported the Life Science market for over
20 years, sourcing personnel for engineering, scientific and commercial roles.
We recruit highly experienced professionals to the biotechnology,
pharmaceutical, diagnostics,
and medical devices industries.
We can provide permanent and contract candidates to the Life
Science industry across the Quality, Clinical, Regulatory/Compliance, and
Engineering disciplines.
If you’re looking for skilled personnel, get
in touch with our dedicated Life Science Recruitment teams to find
out how we can support you.
Are you looking for a new job? Browse
our Life Science vacancies today.